Video Games, Problem-Solving and Self-Efficacy
Part 3: Gaming and Positive Emotions

Part 3 of 3. Continued from The Power of Gameplay for Learning and Growth
The Potential for Positive Emotions
Many people have the image of video games as socially isolating, if not psychologically addicting. Like my friend Kristin demonstrated when she joined her in Wizard101, video games can connect families and friends across time and distances.
DIWO (Do It With Others) or Quests with Friends
Unlike email, texting, or even a phone call, playing a game with someone creates a sense of actually doing something together. Games create a sense of presence — the sense of being in a shared space (Ijsselsteijn, Freeman, & De Ridder, 2001). Games can provide a virtual location for social interaction and relationships beyond home or work because game environments function as Oldenburg’s (1999) “third spaces” or “great good places,” the informal places such as parks and coffee shops that encourage easy sociability and community (e.g., Steinkuehler & Williams, 2006). Multi-player games can be extremely social, with a high percentage of players making lifelong friends and partners (e.g., Cole & Griffiths, 2007).
Optimal Engagement in Flow
Csikszentmihalyi’s (1991) theory of Flow, or optimal engagement, is one of the most prominent concepts of Positive Psychology embraced by game developers (Pavlas, 2010). Several factors contribute to an individual achieving a Flow state. In the context of game development, the most notable is the balance between challenge and skill that allows an individual to be in and maintain the level of engagement defined as Flow (see chart). The skill-challenge balance keeps emotions regulated in a productive way—it allows a player to be challenged enough to avoid boredom and not so much as to trigger anxiety. We can also map this to neuroscience in terms of arousal and the emotions that influence attention, such as conflict, complexity, novelty, and uncertainty or mystery (Rutledge, 2012).
There are other factors that contribute to Flow will sound familiar in the context of video gameplay. These include:
- The integration of clear goals with responsive feedback
- The merging of action and awareness so that the player has complete, focused concentration on the task at hand accompanied by a loss of self-awareness and the passage of time
- The sense of control and confidence
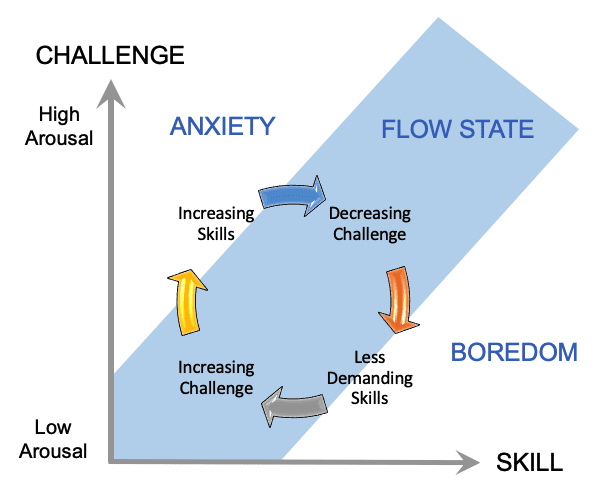 Flow Paths
Flow Paths
Flow is a description of experienced engagement in an activity over time rather than at a single point. The Flow channel represents the player’s experience path of continual interaction between challenge and learning. In well-designed games, players perform at the edge of their competency guided by clear goals and feedback. In the Flow state, the experience of play is fluid and is intrinsically psychologically rewarding independent of scores or in-game successes (Csikszentmihalyi, 1991).
Flow and Learning Zones
The balance of skill and challenge keeps the player’s brain aroused, attention engaged and motivation high. The acquisition of skills to meet each challenge also provides a series of mastery experiences.
Games are designed with structures that create what Vygotsky (1978) called ‘zones of proximal development.’ where learning occurs due to observation and interactions that pull the player forward into more complex and demanding tasks.
Scaffolding is another key concept in Vygotsky’s model of social development. Scaffolding is the on-demand support that allows people to bridge the gap between current and required skills. The responsive feedback in gameplay along with social collaboration and communities provide this scaffolding, facilitating problem-solving and learning retention (Sun, Wang, & Chan, 2011).
A key feature of gameplay is that failure is not ‘failure’ in the schoolyard sense. Failure is equivalent to feedback and the risk of failing is minimal and recovery is easily achieved, encouraging exploration, experimentation and the development of new problem-solving strategies. The process of learning is a socially accepted progression providing social status through achievement in a peer-valued skill and allowing player to capitalize on their strengths.
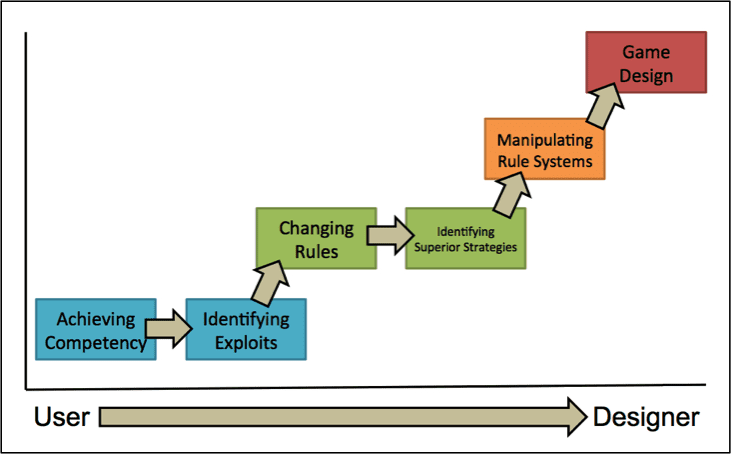 Learning Trajectory
Learning Trajectory
Community creates socially sanctioned support for curiosity and the motivation for scientific inquiry. Gamers frequently transform design issues into empirical questions, collecting data, building and comparing models to predict the system (i.e. decision rules, such as minimaxing or attempting to minimize the possible worst case or maximum loss) (Squire, 2008).
Consumption stimulates mastery and motivates production. Figure 2 shows Squire’s (2008) Trajectory of Player Experience which illustrates the gradual shift from player to designer, blurring the distinction between them similar to what we see happening to the boundaries between consumers and producers of other types of media, as well as breaking down of finite channels of distribution of media content.
Like Squire (2008), Salen and Zimmerman (2004) found that committed players change the rules for their own enjoyment, exploring which rules work and which don’t, and studying the structure that is contributing to meaningful game experience. The exploration becomes an iterative process of breaking, tweaking and modifying where players become more like designers or actually become designers.
Flow or Success
Whether a gaming experience creates a sense of control and competence from a Flow state, connection with an ideal self through immersion, or a sense of accomplishment or ‘fiero’ through skill mastery, these are positive emotions that have longer-term ramifications.
ADHD and learning-challenged children often experience more failures than others, especially in school. Failure, like mastery, impacts perceptions of self-efficacy and both build on previous experience to project future action
According to research in positive psychology, negative and positive emotional experiences are not structural equivalents. Where negative emotions lead to narrowed, self-focused, inflexible or defensive behaviors, positive emotions create upward spirals that promote increased openness and exploratory activity. According to Garland et al. (2010) and research findings based on Fredrickson’s Broaden and Build Theory (Fredrickson, 2004), positive emotions create a cognitive state that is more open, permeable, flexible and social and facilitate cognitive reappraisal of negative circumstances and beliefs (Tugade & Fredrickson, 2004). A buildup of cognitive, psychological, social and physical resources from positive emotions accumulates over time. Evidence suggests that positive emotions expand our mindsets in ways that little by little reshape who we are.
Conclusion
The experience my friend Kristin shared with her son online playing Wizard101 is a good example of how we can reevaluate and reframe our understanding of games as avenues to develop mastery experiences that promote self-efficacy and positive emotions. In a video game, we can:
- Experience emotional and physiological arousal that focuses our attention
- Trigger intrinsic motivation through evidence of accomplishments and successes
- Observe modeled behaviors and receive mentoring through collaboration
- Establish meaningful social connections in communities of play
- Imagine ourselves in new ways with new strengths
- Practice problem-solving and behaviors in low-risk environments
Video games are not a panacea for all of society’s ills but neither are they the cause. Like all tools, from hammers to virtual reality, they can be used for good and for harm. But we can use them for good if we can focus on the psychological fundamentals that underlie both the specific content-driven experience as well the meanings we make of the meta-experience of interactivity and results. We can reframe our point of view about video games recognizing that the act of playing has a positive impact on self-efficacy, thereby increasing resilience, optimism and motivation. We can recognize that all interactive experience hold the potential to be mastery experiences just waiting to be conquered.
References
Bandura, A. (1982). Self-Efficacy Mechanism in Human Agency. American Psychologist, 37(2). Retrieved from
Bandura, A. (2002). Growing primacy of human agency in adaptation and change in the electronic era. [Journal; Peer Reviewed Journal;]. European Psychologist, 7(1), 2-16. doi: 10.1027//1016-9040.7.1.2
Brandt, K. (2012). How Wizard 101 Actually Helped My Son. Simply Stated (March 16). Retrieved from http://simplystated.realsimple.com/2012/03/16/how-i-learned-to-hate-wizard101-a-little-less/
Bruner, J. (1973). Organizaiton of early skilled action. Child Development, 44, 1-11.
Cole, H., & Griffiths, M. (2007). Social Interactions in Massively Multiplayer Online Role-Playing Gamers. CyberPsychology & Behavior, 10(4), 575-583.
Csikszentmihalyi, M. (1991). Flow: The Psychology of Optimal Experience. New York: HarperCollins Publishers.
Cunliffe, A., & Coupland, C. (2012). From hero to villain to hero: Making experience sensible through embodied narrative sensemaking. Human Relations, 65(1), 63-88. doi: 10.1177/0018726711424321
Dagirmanjian, S., Eron, J., & Lund, T. (2007). Narrative solutions: An integration of self and systems perspectives in motivating change. [Journal; Peer Reviewed Journal]. Journal of Psychotherapy Integration, 17(1), 70-92. doi: 10.1037/1053-0479.17.1.70
Erikson, E. (1956). The problem of Edo Identity. Journal of the American Psychoanalytic Association, 4, 56-121.
Fredrickson, B. L. (2004). The broaden-and-build theory of positive emotions. Phil. Trans. Royal Society London, 359, 1367-1377. Retrieved from
Garland, E., Fredrickson, B. L., Kring, A. M., Johnson, D. P., Meyer, P. S., & Penn, D. L. (2010). Upward spirals of positive emotions counter downward spirals of negativity: Insights from the broaden-and-build theory and affective neuroscience on the treatment of emotion dysfunctions and deficits in psychopathology. Clinical Psychology Review, 30(7), 849-864.
Gee, J. P. (2007). What Video Games Have to Teach Us About Learning and Literacy (Revised & Updated) (2nd ed.). New York: Palgrave Macmillan.
Hughes, L., & Cooper, P. (2007). Understanding and Supporting Children with ADHD. Thousand Oaks: Sage.
Ijsselsteijn, W. A., Freeman, J., & De Ridder, H. (2001). Presence: Where Are We? CyberPsychology & Behavior, 4(2), 179-182. Retrieved from http://search.ebscohost.com/login.aspx?direct=true&db=aph&AN=5323497&site=ehost-live
Ito, M. (2009). Introduction. In K. Varnelis (Ed.), Networked Publics (pp. 1-14). Cambridge: MIT.
Klimmt, C., & Hartmann, T. (2009). Effectance, Self-Efficacy, and the Motivation to Play Video Games. In P. Vorderer & J. Bryant (Eds.), Playing Video Games: Motives, Responses and Consequences (pp. 153-169). United Kingdom: Taylor & Francis.
Klimmt, C., Hefner, H., & Vorderer, P. (2009). The video game experience as “true” identification: A theory of enjoyable alterations of players’ self-perception. Communication Theory, 19(4), 351-373.
Krueger, N., & Dickson, P. R. (1994). How Believing in Ourselves Increases Risk Taking: Perceived Self-Efficacy and Opportunity Recognition. Decision Sciences, 25(3), 385-400.
Lave, J., & Wenger, E. (1990). Situated Learning: Legitimate Peripheral Participation IRL Report (Vol. 90-0013). Palo Alto, CA: Institute for Research on Learning.
Lee, J. J., & Hammer, J. (2011). Gamification in Education: What, How, Why Bother? Academic Quarterly, 15(2), 1-5.
Manobi Development Foundation. (2011). Case Studies: In Farming, from http://www.manobi.net/foundation/?M=2&SM=6
Nardi, B., Ly, S., & Harris, J. (2007). Learning Conversations in World of Warcraft. Paper presented at the Hawaii International Conference on Systems Sciences 2007, Big Island, Hawaii.
Oldenburg, R. (1999). The Great Good Place: Cafe´s, Coffee Shops, Community Centers, Beauty Parlors, General Stores, Bars, Hangouts, and How They Get You Through The Day. New York: Marlowe & Company.
Pavlas, D. (2010). A Model of Flow and Play in Game-based Learning: The Impact of Game Characteristics, Player Traits, and Player States. (PhD Dissertation), University of Central Florida, Orlando, FL.
Piaget, J. (1962). Play, Dreams and Imitation in Childhood (C. Gattegno & F. M. Hodgson, Trans.). New York: W.W. Norton & Company.
Przybylski, A. K., Weinstein, N., Murayama, K., Lynch, M. F., & Ryan, R. M. (2012). The Ideal Self at Play : The Appeal of Video Games That Let You Be All You Can Be. Psychological Science, 23, 69-76.
Reeves, B., Malone, T. W., & O’Driscoll, T. (2008). Leadership’s Online Labs. Harvard Business Review, May, 1-10.
Rutledge, P. B. (2012). Augmented Reality: Brain-based Persuasion Model. Paper presented at the 2012 EEE International Conference on e-Learning, e-Business, Enterprise Information Systems, and e-Government, Las Vegas, NV.
Salen, K., & Zimmerman, E. (2004). Rules of Play: Game Design Fundamentals. Cambridge, MA: The MIT Press.
Shirky, C. (2008). Here Comes Everybody. New York: Penguin Books.
Smith, D. S., & Nagle, R. (1995). Self-Perceptions and Social Comparisons Among Children with LD. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 28(6), 364-371.
Squire, K. R. (2008). Open-Ended Video Games: A Model for Developing Learning. In K. Salen (Ed.), The Ecology of Games: Connecting Youth , Games, and Learning (pp. 167-198). Cambridge. MA: MIT.
Steinkuehler, C. (2004). Learning in Massively Multiplayer Online Games. Paper presented at the ICLS ’04 Proceedings of the 6th international conference on Learning sciences Santa Monica, CA. Conference Paper retrieved from http://jcmc.indiana.edu/vol11/issue4/steinkuehler.html
Steinkuehler, C., & Williams, D. (2006). Where Everybody Knows Your (Screen) Name: Online Games as “Third Places”. Journal of Computer Mediated Communication, 11(4). Retrieved from http://jcmc.indiana.edu/vol11/issue4/steinkuehler.html
Sun, C.-T., Wang, D.-Y., & Chan, H.-L. (2011). How digital scaffolds in games direct problem-solving behaviors. Computers & Education, 57(3), 2118-2125. doi: 10.1016/j.compedu.2011.05.022
Tugade, M., & Fredrickson, B. L. (2004). Resilient Individuals Use Positive Emotions to Bounce Back From Negative Emotional Experiences. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 86(2), 320-333. Retrieved from
Van Eck, R. (2006). Digital Game-Based Learning: It’s Not Just the Digital Natives Who Are Restless…. EDUCAUSE Review, 41(2).
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in Society. In M. Cole, V. John-Steiner, S. Scribner & E. Souberman (Eds.). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Weisler, A., & McCall, R. B. (1976). Exploration and Play: Resume and Redirection. American Psychologist, July, 492-508.
 Dr. Pamela Rutledge is available to reporters for comments on the psychological and social impact of media and technology on individuals, society, organizations and brands.
Dr. Pamela Rutledge is available to reporters for comments on the psychological and social impact of media and technology on individuals, society, organizations and brands.
Comments are closed.